ENERGY METABOLISM
What is exercise?
Exercise is any bodily activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness.
It is performed for various reasons including strengthening muscles and the cardiovascular system, honing athletic skills, weight loss or maintenance, as well as for the purpose of enjoyment. Frequent and regular physical exercise boosts the immune system, and helps prevent the "diseases of affluence" such as heart disease, cardiovascular disease, Type 2 diabetes and obesity.
It also improves mental health, helps prevent depression.
Metabolism
It is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments.
Metabolism is usually divided into two categories. Catabolism, that breaks down organic matter and harvests energy by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism that uses energy to construct components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids.
Anaerobic metabolism
Is the creation of energy through the combustion of carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. This occurs when your lungs cannot put enough oxygen into the bloodstream to keep up with the demands of your muscles for energy. It generally is used only for short bursts of activity, such as when you go for a sprint when running or cycling or when you are lifting heavy weights.
When there isn't enough oxygen in the bloodstream, glucose and glycogen cannot be fully broken down to carbon dioxide and water. Instead, lactic acid is produced, which can build up in the muscles and degrade muscle function.
Aerobic metabolism
Is the way your body creates energy through the combustion of carbohydrates, amino acids, and fats in the presence of oxygen. Combustion means burning, which is why this is called burning sugars, fats, and proteins for energy. Aerobic metabolism is used for the sustained production of energy for exercise and other body functions. Examples of exercises that use aerobic metabolism include walking, running, or cycling with sustained effort.
How to avoid injuries
- Listen to body signals.
- Pay attention to sharp pain which signals that something is probably wrong. Dress for the weather.
- Don’t just be a weekend exerciser.
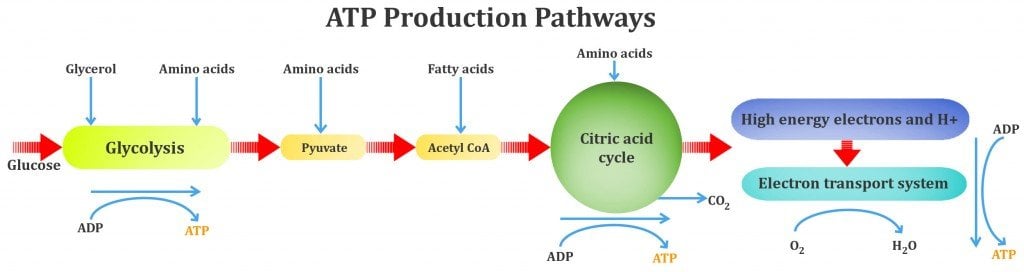
The two processes are clearly intertwined, and equally important. Without aerobic respiration, we would lack the constant sources of energy needed to walk, breathe, work, speak and drive a car. Without anaerobic respiration, our ability to snap into action, such as during a fight-or-flight scenario, would be severely compromised. All in all, we should be eternally grateful for both sides of the metabolic pathway, and the clever path of evolution that allows us to live!